Label the steps and components of the polymerase chain reaction – Delving into the intricacies of the polymerase chain reaction (PCR), this exploration unveils the fundamental principles, essential components, and wide-ranging applications of this groundbreaking technique. PCR has revolutionized fields from diagnostics to genetic engineering, and this comprehensive guide unravels the steps and components that make it possible.
PCR’s ability to amplify specific DNA sequences has transformed our understanding of genetics and enabled countless advancements in biotechnology. This in-depth analysis provides a detailed roadmap of the PCR process, empowering readers with a thorough comprehension of its mechanisms and applications.
Overview of Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)
Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a powerful molecular biology technique used to amplify specific regions of DNA. It has revolutionized various fields, including diagnostics, forensics, genetic engineering, and research.
The fundamental principle of PCR involves repeatedly copying a target DNA sequence through a series of temperature-controlled cycles.
Steps of PCR
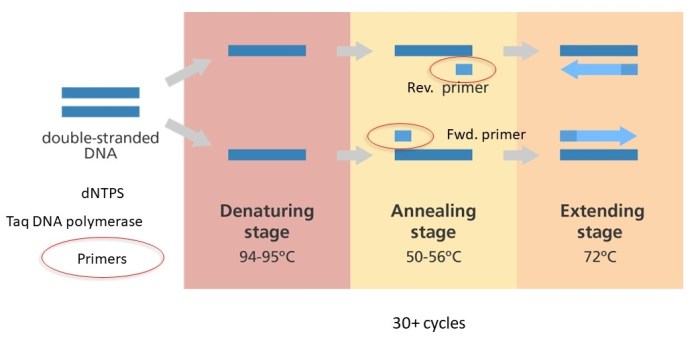
| Step | Description | Purpose | Temperature |
|---|---|---|---|
| Denaturation | DNA template strands are separated by heating | Breaks hydrogen bonds between complementary strands | 94-98°C |
| Annealing | Primers bind to complementary sequences on the DNA template | Creates a template for DNA polymerase | 45-65°C |
| Extension | DNA polymerase extends the primers, synthesizing new DNA strands | Amplifies the target DNA sequence | 72°C |
Components of PCR
- DNA template:The DNA containing the target sequence to be amplified
- Primers:Short DNA sequences complementary to the ends of the target sequence
- DNA polymerase:An enzyme that synthesizes new DNA strands
- Nucleotides:The building blocks of DNA (dNTPs)
- Buffer solution:Provides optimal pH and ionic conditions for PCR
Optimization of PCR: Label The Steps And Components Of The Polymerase Chain Reaction
The efficiency of PCR can be affected by various factors, including:
- Primer concentrations
- Annealing temperatures
- Cycle parameters
Optimization strategies involve adjusting these parameters to achieve optimal amplification and minimize nonspecific products.
Applications of PCR
- Diagnostics:Detecting pathogens, genetic disorders, and mutations
- Forensics:DNA fingerprinting and identification
- Genetic engineering:Creating genetically modified organisms
- Research:Studying gene expression, evolution, and genetic diversity
PCR has become an indispensable tool in these fields, providing insights into the molecular basis of life.
Clarifying Questions
What is the purpose of the denaturation step in PCR?
The denaturation step separates the double-stranded DNA template into single strands, allowing the primers to bind during the annealing step.
What is the optimal temperature range for the annealing step?
The optimal temperature range for the annealing step varies depending on the primers used, but typically falls between 55-65°C.
What is the role of DNA polymerase in PCR?
DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands complementary to the template strands, extending the primers during the extension step.