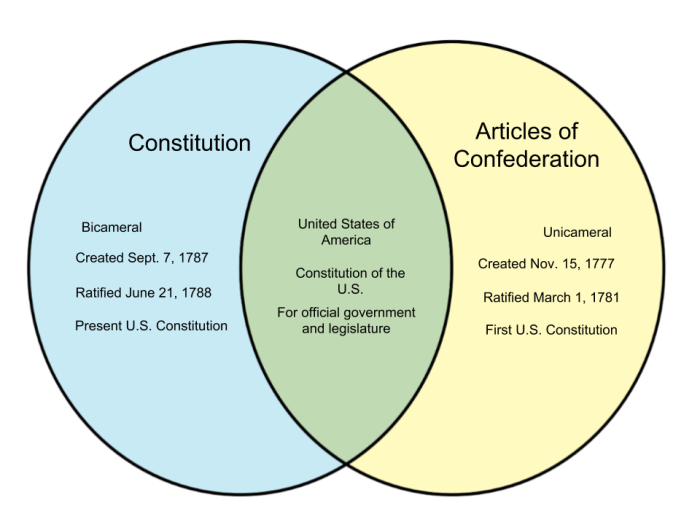
At the heart of the Articles of Confederation and Constitution Venn Diagram lies a captivating tale of America’s constitutional development. This diagram illuminates the key similarities and differences between these two foundational documents, offering a profound understanding of their impact on the nation’s political landscape.
The Articles of Confederation, ratified in 1781, established a loose confederation of states with limited federal authority. In contrast, the Constitution, adopted in 1789, created a stronger national government with expanded powers. By examining these documents side-by-side, we gain insights into the fundamental principles that have shaped American governance for centuries.
Articles of Confederation and Constitution Venn Diagram
The Articles of Confederation and the Constitution are two fundamental documents in the history of the United States. The Articles of Confederation established the first national government of the United States, while the Constitution replaced the Articles and created a stronger and more centralized government.
A Venn diagram can be used to compare and contrast the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution. The Venn diagram will have two overlapping circles, one representing the Articles of Confederation and the other representing the Constitution. The area where the circles overlap represents the similarities between the two documents, while the areas outside the overlap represent the differences.
Structure of the Venn Diagram
| Feature | Articles of Confederation | Constitution | Both | Neither |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Powers of the federal government | Limited | Expanded | ||
| Powers of the states | Reserved | Limited | ||
| Individual rights | Protected | Strengthened |
Analysis of Key Features, Articles of confederation and constitution venn diagram
Powers of the federal government
- Under the Articles of Confederation, the federal government had very limited powers. It could not tax, regulate commerce, or raise an army.
- Under the Constitution, the federal government was given expanded powers, including the power to tax, regulate commerce, and raise an army.
Powers of the states
- Under the Articles of Confederation, the states retained most of their powers.
- Under the Constitution, the states were given limited powers, such as the power to regulate local affairs.
Individual rights
- Both the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution protected individual rights, such as the right to a fair trial and the right to freedom of speech.
- However, the Constitution strengthened individual rights by adding a Bill of Rights.
Impact of the Changes
Expansion of federal power
The Constitution expanded the powers of the federal government compared to the Articles of Confederation. This gave the federal government more authority to regulate the economy, protect the nation from foreign threats, and promote the general welfare.
Balance of power
The Constitution also changed the balance of power between the federal government and the states. The federal government was given more power, while the states were given less power.
Strengthening of individual rights
The Constitution strengthened individual rights and protections. The Bill of Rights added to the Constitution a number of important rights, such as the right to a fair trial, the right to freedom of speech, and the right to bear arms.
FAQ Section
What is the main difference between the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution?
The main difference lies in the extent of federal power. The Articles of Confederation created a loose confederation with limited federal authority, while the Constitution established a stronger national government with expanded powers.
How did the Constitution strengthen individual rights?
The Constitution incorporated the Bill of Rights, which guarantees fundamental freedoms and protections for individuals, such as freedom of speech, religion, and the right to bear arms.